Role of Classroom Assessment and Feedback Techniques in Improving Learning Outcomes at Secondary Level
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62497/irjed.169Keywords:
classroom assessment, feedback techniques, learning outcomes, secondary education, formative assessment, summative assessment, teaching effectiveness, academic performance, peer assessment, student engagement, educational qualityAbstract
Background: Classroom assessment and feedback play a pivotal role in promoting effective teaching and learning, particularly in secondary education. Continuous assessment provides valuable insights into students’ academic progress, while timely and constructive feedback enhances motivation, engagement, and overall achievement. Understanding how assessment and feedback techniques influence student learning outcomes is essential for improving teaching effectiveness in schools.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the relationship between classroom assessment practices, feedback techniques, and learning outcomes among secondary school students. It focused on how formative and summative assessment methods, combined with different feedback approaches, contribute to students’ academic performance and engagement.
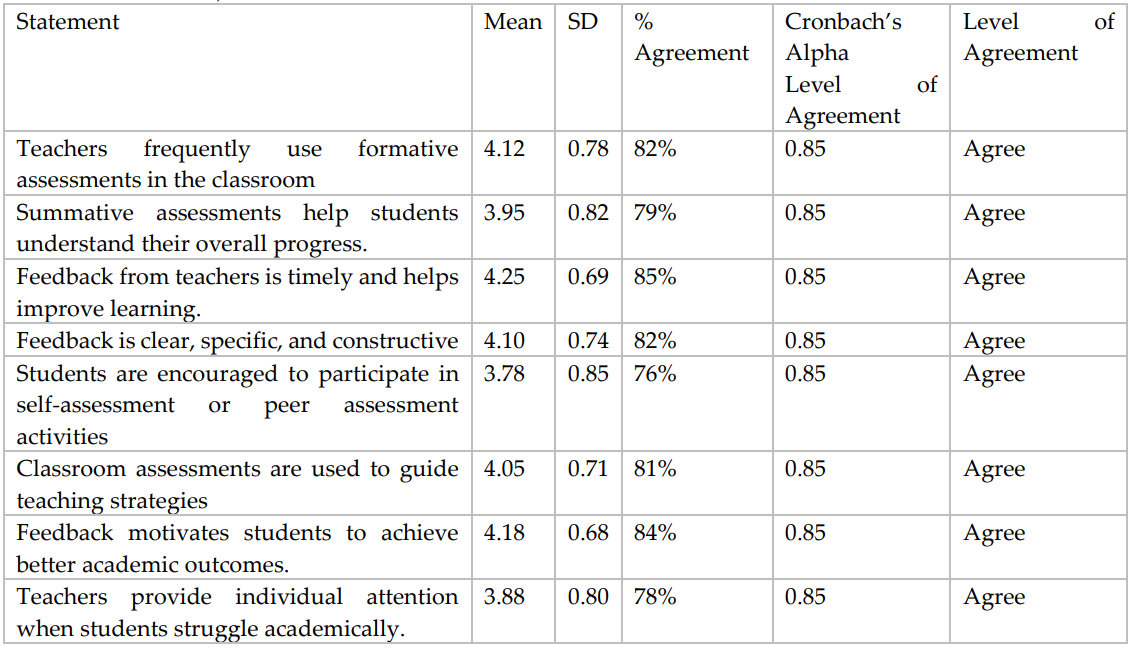
Materials and Methods: A quantitative descriptive-comparative research design was employed, involving 180 participants (150 students and 30 teachers) from both public and private secondary schools. Data were collected through structured questionnaires and classroom observations, and analyzed using descriptive statistics, comparative tests, and Pearson correlation via SPSS. The research instruments demonstrated strong reliability (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.85).
Results: Findings revealed a strong positive correlation between feedback techniques and learning outcomes (r = 0.76, p < 0.01), and between formative assessments and academic performance (r = 0.72, p < 0.01). Teachers and students both perceived feedback as clear, timely, and motivating. However, peer and self-assessment practices were less frequently implemented, indicating areas for professional development.
Conclusion: The study concludes that effective classroom assessment and feedback practices significantly enhance secondary school students’ learning outcomes. Integrating formative assessment, constructive feedback, and reflective evaluation promotes deeper learning and sustained achievement. It is recommended that teachers receive continuous professional training to strengthen assessment literacy and feedback delivery.
References
Ahmed, M., Butt, M., Khan, A. M., & Habib, Z. (2022). Determining the changes needed to improve classroom assessment: An analysis of secondary schools in Pakistan. KEDI Journal of Educational Policy, 19(2), 97–116. https://doi.org/10.22804/kjep.2022.19.2.005
Ali, S. K., Shah, S. K., Butt, M., Khan, A. M., & Habib, Z. (2022). Assessing feedback practices in classroom assessment at federal government educational institutions of Lahore, Pakistan. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education, 11(4), 1825–1832.https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v11i4.22024
Black, P. (2003). Assessment for learning: Putting it into practice. Open University Press. http://www.mcgraw-hill.co.uk/html/0335212972.html
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (1998). Assessment and classroom learning. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, 5(1), 7–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969595980050102
Boud, D., Cohen, R., & Sampson, J. (1999). Peer learning and assessment. Assessment & evaluation in higher education, 24(4), 413-426. https://doi.org/10.1080/0260293990240405
Brookhart, S. M. (2008). Feedback that fits. Educational Leadership, 66(1), 36–40. Retrieved from https://www.ascd.org/el/articles/feedback-that-fits
Brookhart, S. M. (2019). How to give effective feedback to your students. Second Edition. ASCD. https://files.ascd.org/staticfiles/ascd/pdf/siteASCD/publications/books/How-to-Give-Effective-Feedback-to-Your-Students-2nd-Edition-sample-chapters.pdf
Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (4th ed.). SAGE Publications. Retrieved from https://study.sagepub.com/creswellrd4e
Emmer, E. T., & Sabornie, E. J. (Eds.). (2014). Handbook of classroom management (2nd ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203074114
Gibbs, G., & Simpson, C. (2005). Conditions under which assessment supports students’ learning. Learning and teaching in higher education, (1), 3-31. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237063306_Conditions_Under_Which_Assessment_Supports_Students'_Learning
Hattie, J., & Timperley, H. (2007). The power of feedback. Review of educational research, 77(1), 81-112. https://doi.org/10.3102/003465430298487
Hounsell, D., McCune, V., Hounsell, J., & Litjens, J. (2008). The quality of guidance and feedback to students. Higher Education Research & Development, 27(1), 55-67. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360701658765
Khan, W. A. (2020). Comparative analysis of the assessment practices in public and private schools: A case study of Lahore and Kasur districts in Punjab, Pakistan. Proceedings of the 2nd International Academic Conference on Education, Teaching and Learning, 16. https://doi.org/10.33422/2nd.iacetl.2020.12.16
Nicol, D. J., & Macfarlane-Dick, D. (2006). Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: A model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education, 31(2), 199–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070600572090
Sadler, D. R. (1989). Formative assessment and the design of instructional systems. Instructional Science, 18(2), 119–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00117714
Shute, V. J. (2008). Focus on formative feedback. Review of Educational Research, 78(1), 153–189. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654307313795
Stiggins, R. J. (2005). From formative assessment to assessment for learning: A path to success in standards-based schools. Phi Delta Kappan, 87(4), 324–328. https://doi.org/10.1177/003172170508700414
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
