The Gut–Oral Axis: The Impact of Oral Dysbiosis on Systemic Inflammation and Chronic Diseases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62497/irjcs.90Keywords:
oral dysbiosis, systemic inflammation, chronic disease, oral microbiome, gut-oral axis, inflammatory markers, microbiota diversityAbstract
Introduction: The gut-oral axis has become an important connection showing how problems with oral bacteria can lead to inflammation in the body and long-term diseases. This study aimed to investigate the association between oral dysbiosis, systemic inflammatory markers, and the prevalence of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Methodology: This cross-sectional study was conducted over 12 months at Khyber College of Dentistry, Peshawar. A total of 126 patients with at least one chronic disease (type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, rheumatoid arthritis, or inflammatory bowel disease) were enrolled. Oral health status was assessed using clinical indices and saliva samples for microbial analysis. Systemic inflammation was evaluated via hs-CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α levels. Statistical analyses included chi-square tests, Pearson correlation, and multivariate regression.
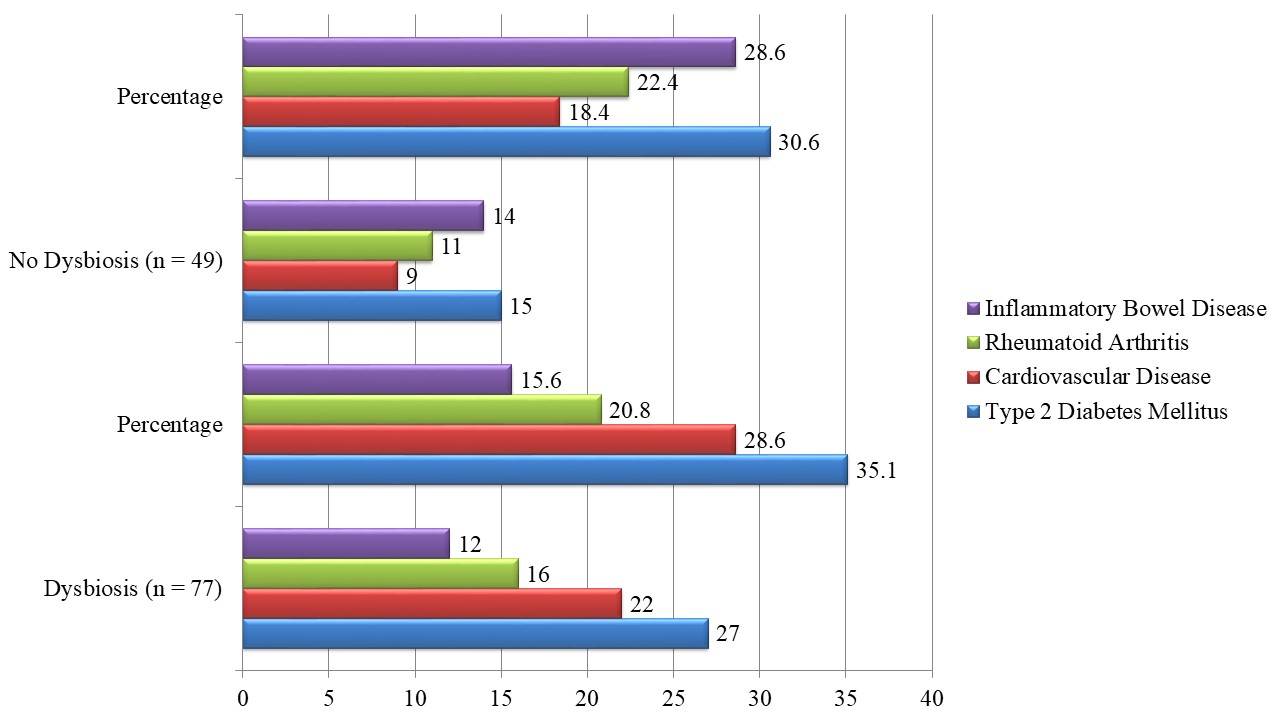
Results: Oral dysbiosis was present in 64.3% of participants. Dysbiosis was significantly associated with elevated hs-CRP (mean 5.8 ± 2.1 mg/L), IL-6 (14.6 ± 4.2 pg/mL), and TNF-α (18.1 ± 5.5 pg/mL) (p < 0.001). Patients with a low Shannon diversity index (<2.0) showed markedly higher systemic inflammation. Oral hygiene parameters such as plaque index (PI ≥ 2) and bleeding on probing were independent predictors of dysbiosis (p < 0.05). Strong associations were noted between oral dysbiosis and type 2 diabetes (p = 0.002) and cardiovascular disease (p = 0.005), with weaker but notable links to rheumatoid arthritis.
Conclusion: Oral dysbiosis is significantly correlated with systemic inflammation and appears to influence the burden of chronic disease. Improving oral microbial health may offer a novel approach for reducing systemic inflammation and managing chronic inflammatory disorders.
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Innovative Research Journal of Clinical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
